Pages
THE WORLD OF COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY
Sunday, 21 July 2013
HOW TO CREAT BACKDOOR IN WINDOW SEVEN
Thursday, 18 July 2013
Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
Wine is a great tool for Linux users who want to install and run Windows applications under Linux. Tonight I decided to test Wine and therefore searched about downloading and installing Wine on my Red Hat Enterprise Linux. So its time for you to get ready for an eventful journey towards Wine.
The installation process is quite easy. Wine package is included in RHEL so all you need is to issue the following command:
- yum install wine
Now just be patient till it get installed. Once you have it installed get an exe file to test Wine. So I downloaded Firefox8 and give it a try with Wine. Now open your terminal. Don’t try to run it from CLI mode. To run an exe issue the following command:
- wine yourfilepath.exe( for example I issued wine /root/Desktop/Firefox\ Setup\ 8.0.exe
And what I see is that the installation process has begun. Wow! I am running exe files in Linux.

Sunday, 14 July 2013
To Password Protect Folders with Folder Protector?
- Step 1. Select folders for protect
- Copy Folder Protector (lockdir.exe) to the folder you want
to protect or drag and drop the folder you want to protect in the operation
window of Folder Protector for adding the folder to protect.
step 2. Send Password to protect selected folder
- Make settings in Settings window and then right-click on the folder and
navigate to "Folder Protector" option to password protect it.
- a. Click on the ">>" Button on the right side of the
main window.
b. Type a password hint to help you remember your password.
- Remember that anyone unprotected this folder will be able to see the
password hint.
c. Set an e-mail address to help you retrieve password. The program will remember this e-mail address if you click on "Save as default e-mail".
Part II. Unprotect a Folder
- Three different unprotection modes
- Virtual Drive: Access your data in a virtual drive without
extracting the data, which means the folder will be reprotected automatically as
soon as you close the explorer window.
- Temporary: Show a restore window on your taskbar after
unprotection, which allows you restore protection easily.
- Complete: Completely unprotect your folder. You need to run
Folder Protector again and enter a new password to protect the folder if you
wish to gain folder protection again.
- Temporary unprotection Window.
Saturday, 13 July 2013
RSA Algorithm Example
RSA Algorithm Example
- Choose p = 3 and q = 11
- Compute n = p * q = 3 * 11 = 33
- Compute φ(n) = (p - 1) * (q - 1) = 2 * 10 = 20
- Choose e such that 1 < e < φ(n) and e and n are coprime. Let e = 7
- Compute a value for d such that (d * e) % φ(n) = 1. One solution is d = 3 [(3 * 7) % 20 = 1]
- Public key is (e, n) => (7, 33)
- Private key is (d, n) => (3, 33)
- The encryption of m = 2 is c = 27 % 33 = 29
- The decryption of c = 29 is m = 293 % 33 = 2
Friday, 12 July 2013
Cryptographic Algorithms
THE CRYPTOGRAPHY GUIDE
| |
Cryptographic Algorithms
DES This is the 'Data Encryption Standard'. This is a cipher that operates on 64-bit blocks of data, using a 56-bit key. It is a 'private key' system. Further Details on the DES Algorithm RSA RSA is a public-key system designed by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman. Further Details on the RSA Algorithm HASH A 'hash algorithm' is used for computing a condensed representation of a fixed length message/file. This is sometimes known as a 'message digest', or a 'fingerprint'.. MD5 MD5 is a 128 bit message digest function. It was developed by Ron Rivest. Further Details on the MD5 Algorithm AES This is the Advanced Encryption Standard (using the Rijndael block cipher) approved by NIST. SHA-1 SHA-1 is a hashing algorithm similar in structure to MD5, but producing a digest of 160 bits (20 bytes).Because of the large digest size, it is less likely that two different messages will have the same SHA-1 message digest. For this reason SHA-1 is recommended in preference to MD5. HMAC HMAC is a hashing method that uses a key in conjunction with an algorithm such as MD5 or SHA-1. Thus one can refer to HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA1 | |
Wednesday, 10 July 2013
Windows XP Network configuration
Windows XP Professional
- On some installations the interface will be called Local Area Connection and on others it will be called Network Bridge. On our system it is called Network Bridge. Right-click on Network Bridge -> Properties.
- The Network Bridge Configuration, or Local Area Connection, panel is used to set TCP/IP protocol settings. In This connection uses the following items: box, click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click on Properties.The default setting is DHCP-enabled operation (i.e.“Obtain an IP address automatically”).Many network administrators will want to use DHCP to configure all client TCP/IP protocol stack settings.If it is necessary to provide a fixed IP address, click on “Use the following IP address” and enter the IP Address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway address in the boxes provided.
- Click the Advanced button to proceed with TCP/IP configuration. This opens a panel in which it is possible to create additional IP addresses for this interface. The technical name for the additional addresses is IP aliases, and additionally this panel permits the setting of more default gateways (routers). In most cases where DHCP is used, it will not be necessary to create additional settings.
Fixed settings may be required for DNS and WINS if these settings are not provided automatically via DHCP.
- Click the DNS tab to add DNS server settings. The example system uses manually configured DNS settings. When finished making changes, click the OK to commit the settings.DNS Configuration.
- Click the WINS tab to add manual WINS server entries. This step demonstrates an example system that uses manually configured WINS settings. When finished making changes, click OK to commit the settings.WINS Configuration
Network configuration in Linux
Tuesday, 9 July 2013
OOPs Concepts
| OOPs – Object Oriented Programming System Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses “Objects “and their interactions to design applications and computer programs. There are different types of OOPs are used, they are
1) Object :Object is the basic unit of object-oriented programming. Objects are identified by its unique name. An object represents a particular instance of a class. There can be more than one instance of an object. Each instance of an object can hold its own relevant data.
An Object is a collection of data members and associated member functions also known as methods.
For example whenever a class name is created according to the class an object should be created without creating object can’t able to use class.
The class of Dog defines all possible dogs by listing the characteristics and behaviors they can have; the object Lassie is one particular dog, with particular versions of the characteristics. A Dog has fur; Lassie has brown-and-white fur.
2) Class :
Classes are data types based on which objects are created. Objects with similar properties and methods are grouped together to form a Class. Thus a Class represents a set of individual objects. Characteristics of an object are represented in a class as Properties. The actions that can be performed by objects become functions of the class and is referred to as Methods.
For example consider we have a Class of Cars under which Santro Xing, Alto and WaganR represents individual Objects. In this context each Car Object will have its own, Model, Year of Manufacture, Colour, Top Speed, Engine Power etc., which form Properties of the Car class and the associated actions i.e., object functions like Start, Move, Stop form the Methods of Car Class.No memory is allocated when a class is created. Memory is allocated only when an object is created, i.e., when an instance of a class is created.
|
Inheritance is the process of forming a new class from an existing class or base class.
- Single level inheritance
- Multi-level inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
- Hierarchial inheritance
Polymorphism allows routines to use variables of different types at different times. An operator or function can be given different meanings or functions. Polymorphism refers to a single function or multi-functioning operator performing in different ways.
It contains a concept of Inheritance and Polymorphism.
Setup The Timezone
HowTo: Linux Server Change OR Setup The Timezone
Unix time, or POSIX time, is a system for describing points in time: it is the number of seconds elapsed since midnight UTC on the morning of January 1, 1970, not counting leap seconds. The definition for time zones can be written in short form as UTC±n (or GMT±n), where n is the offset in hours. You can use the following commands:
Command to change the Linux timezone
If you are using Fedora / RHEL / Cent OS Linux
# redhat-config-dateOR type setup and select time zone configuration. This tool is recommended for remote ssh text based sessions.
# setupSelect timezone configuration
Just follow on screen instructions to change the timezone.
If you are using Debian / Ubuntu Linux
# dpkg-reconfigure tzdataAgain, just follow on screen instructions.
Set timezone using /etc/localtime configuration file [any Linux distro]
Generic procedure to change timezone under Linux
# cd /etcCreate a symlink to file localtime:
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/EST localtimeOR some distro use /usr/share/zoneinfo/dirname/zonefile format (Red hat and friends):
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/EST localtimeOR if you want to set up it to IST (Asia/Calcutta):
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta localtimePlease note that in above example you need to use directory structure i.e. if you want to set the timezone to Calcutta (India) which is located in the Asia directory.
How do I verify new settings?
$ dateOutput:
Tue Aug 27 14:46:08 EST 2006
How do I use of environment variable called TZ?
$ export TZ=America/Los_Angeles
$ dateSample Output:
Thu Aug 27 11:10:08 PST 2006
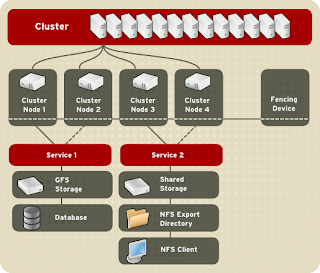
Cluster configuration
Red Hat Cluster allows you to connect a group of computers (called nodes or members) to work together as a cluster. It provides a wide variety of ways to configure hardware and software to suit your clustering needs (for example, a cluster for sharing files on a GFS file system or a cluster with high-availability service failover). This book provides information about how to use configuration tools to configure your cluster and provides considerations to take into account before deploying a Red Hat Cluster. To ensure that your deployment of Red Hat Cluster fully meets your needs and can be supported, consult with an authorized Red Hat representative before you deploy it.
List of web browsers
List of web browsers
History:-
This is a table of personal computer web browsers by year of release of major version, in chronological order, with the approximate number of worldwide Internet users in millions. Note that Internet user data is related to the entire market, not the versions released in that year. The increased growth of the Internet in the 1990s and 2000s means that current browsers with small market shares have more total users than the entire market early on. For example, 90% market share in 1997 would be roughly 60 million users, but by the start of 2007 9% market share would equate to over 90 million users.
| Year | Web browsers | Internet users (in millions)[1][2][3] |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | WorldWideWeb (Nexus) | 4 |
| 1992 | ViolaWWW, Erwise, MidasWWW, MacWWW (Samba) | 7 |
| 1993 | Mosaic, Cello,[4] Lynx 2.0, Arena, AMosaic 1.0 | 10 |
| 1994 | IBM WebExplorer, Netscape Navigator, SlipKnot 1.0, MacWeb, IBrowse, Agora (Argo), Minuet | 20 |
| 1995 | Internet Explorer 1, Netscape Navigator 2.0, OmniWeb, UdiWWW,[5] Internet Explorer 2, Grail | 16-39 |
| 1996 | Arachne 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.0, Netscape Navigator 3.0, Opera 2.0, PowerBrowser 1.5,[6] Cyberdog, Amaya 0.9,[7] AWeb, Voyager | 36-73 |
| 1997 | Internet Explorer 4.0, Netscape Navigator 4.0, Netscape Communicator 4.0, Opera 3.0,[8] Amaya 1.0[7] | 70-118 |
| 1998 | iCab, Mozilla | 147-184 |
| 1999 | Amaya 2.0,[7] Mozilla M3, Internet Explorer 5.0 | 248-278 |
| 2000 | Konqueror, Netscape 6, Opera 4,[9] Opera 5,[10] K-Meleon 0.2, Amaya 3.0,[7] Amaya 4.0[7] | 361-396 |
| 2001 | Internet Explorer 6, Galeon 1.0, Opera 6,[11] Amaya 5.0[7] | 513-499 |
| 2002 | Netscape 7, Mozilla 1.0, Phoenix 0.1, Links 2.0, Amaya 6.0,[7] Amaya 7.0[7] | 587-659 |
| 2003 | Opera 7,[12] Safari 1.0, Epiphany 1.0, Amaya 8.0[7] | 719-771 |
| 2004 | Firefox 1.0, Netscape Browser, OmniWeb 5.0 | 817-897 |
| 2005 | Safari 2.0, Netscape Browser 8.0, Opera 8,[13] Epiphany 1.8, Amaya 9.0,[7] AOL Explorer 1.0, Maxthon 1.0, Shiira 1.0 | 1018-1022 |
| 2006 | SeaMonkey 1.0, K-Meleon 1.0, Galeon 2.0, Camino 1.0, Firefox 2.0, Avant 11, iCab 3, Opera 9,[14] Internet Explorer 7 | 1093-1150 |
| 2007 | Maxthon 2.0, Netscape Navigator 9, NetSurf 1.0, Flock 1.0, Safari 3.0, Conkeror | 1319-1364 |
| 2008 | Konqueror 4, Safari 3.1, Opera 9.5,[15] Firefox 3, Amaya 10.0,[7] Flock 2, Chrome 1, Amaya 11.0[7] | 1574-1556 |
| 2009 | Internet Explorer 8, Chrome 2-3, Safari 4, Opera 10,[16] SeaMonkey 2, Camino 2, Firefox 3.5 | 1802-1743 |
| 2010 | K-Meleon 1.5.4, Firefox 3.6, Chrome 4-8, Opera 10.50,[17] Safari 5, xxxterm, Opera 11 | 1971-2012 |
| 2011 | Chrome 9-16, Firefox 4-9, Internet Explorer 9, Maxthon 3.0, SeaMonkey 2.1-2.3, Opera 11.50, Safari 5.1 | 2,267-2264 |
| 2012 | Chrome 17-23, Firefox 10-17, Internet Explorer 10, Opera 12, Safari 6 | 2,405 |
Saturday, 6 July 2013
A Comparison of Network Models
A Comparison of Network Models
Blog Archive
-
▼
2013
(25)
-
▼
July
(15)
- HOW TO CREAT BACKDOOR IN WINDOW SEVEN
- Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
- To Password Protect Folders with Folder Protector?
- RSA Algorithm Example
- Cryptographic Algorithms
- Windows XP Network configuration
- Network configuration in Linux
- OOPs Concepts
- Setup The Timezone
- Cluster configuration
- List of web browsers
- A Comparison of Network Models
- CLOUD COMPUTING
- Basic Linux Commands
- STEGANOGRAPHY
-
▼
July
(15)
About Me
Sample Text
Sample Text
Sample text
You can replace this text by going to "Layout" and then "Page Elements" section. Edit " About "
HOW TO CREAT BACKDOOR IN WINDOW SEVEN
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 04:01 0 comments Sunday, 21 July 2013
Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 01:09 0 comments Thursday, 18 July 2013
Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
Wine is a great tool for Linux users who want to install and run Windows applications under Linux. Tonight I decided to test Wine and therefore searched about downloading and installing Wine on my Red Hat Enterprise Linux. So its time for you to get ready for an eventful journey towards Wine.
The installation process is quite easy. Wine package is included in RHEL so all you need is to issue the following command:
- yum install wine
Now just be patient till it get installed. Once you have it installed get an exe file to test Wine. So I downloaded Firefox8 and give it a try with Wine. Now open your terminal. Don’t try to run it from CLI mode. To run an exe issue the following command:
- wine yourfilepath.exe( for example I issued wine /root/Desktop/Firefox\ Setup\ 8.0.exe
And what I see is that the installation process has begun. Wow! I am running exe files in Linux.

To Password Protect Folders with Folder Protector?
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 23:49 0 comments Sunday, 14 July 2013
- Step 1. Select folders for protect
- Copy Folder Protector (lockdir.exe) to the folder you want
to protect or drag and drop the folder you want to protect in the operation
window of Folder Protector for adding the folder to protect.
step 2. Send Password to protect selected folder
- Make settings in Settings window and then right-click on the folder and
navigate to "Folder Protector" option to password protect it.
- a. Click on the ">>" Button on the right side of the
main window.
b. Type a password hint to help you remember your password.
- Remember that anyone unprotected this folder will be able to see the
password hint.
c. Set an e-mail address to help you retrieve password. The program will remember this e-mail address if you click on "Save as default e-mail".
Part II. Unprotect a Folder
- Three different unprotection modes
- Virtual Drive: Access your data in a virtual drive without
extracting the data, which means the folder will be reprotected automatically as
soon as you close the explorer window.
- Temporary: Show a restore window on your taskbar after
unprotection, which allows you restore protection easily.
- Complete: Completely unprotect your folder. You need to run
Folder Protector again and enter a new password to protect the folder if you
wish to gain folder protection again.
- Temporary unprotection Window.
RSA Algorithm Example
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 02:07 1 comments Saturday, 13 July 2013
RSA Algorithm Example
- Choose p = 3 and q = 11
- Compute n = p * q = 3 * 11 = 33
- Compute φ(n) = (p - 1) * (q - 1) = 2 * 10 = 20
- Choose e such that 1 < e < φ(n) and e and n are coprime. Let e = 7
- Compute a value for d such that (d * e) % φ(n) = 1. One solution is d = 3 [(3 * 7) % 20 = 1]
- Public key is (e, n) => (7, 33)
- Private key is (d, n) => (3, 33)
- The encryption of m = 2 is c = 27 % 33 = 29
- The decryption of c = 29 is m = 293 % 33 = 2
Cryptographic Algorithms
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 04:07 0 comments Friday, 12 July 2013
THE CRYPTOGRAPHY GUIDE
| |
Cryptographic Algorithms
DES This is the 'Data Encryption Standard'. This is a cipher that operates on 64-bit blocks of data, using a 56-bit key. It is a 'private key' system. Further Details on the DES Algorithm RSA RSA is a public-key system designed by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman. Further Details on the RSA Algorithm HASH A 'hash algorithm' is used for computing a condensed representation of a fixed length message/file. This is sometimes known as a 'message digest', or a 'fingerprint'.. MD5 MD5 is a 128 bit message digest function. It was developed by Ron Rivest. Further Details on the MD5 Algorithm AES This is the Advanced Encryption Standard (using the Rijndael block cipher) approved by NIST. SHA-1 SHA-1 is a hashing algorithm similar in structure to MD5, but producing a digest of 160 bits (20 bytes).Because of the large digest size, it is less likely that two different messages will have the same SHA-1 message digest. For this reason SHA-1 is recommended in preference to MD5. HMAC HMAC is a hashing method that uses a key in conjunction with an algorithm such as MD5 or SHA-1. Thus one can refer to HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA1 | |
Windows XP Network configuration
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 05:18 0 comments Wednesday, 10 July 2013
Windows XP Professional
- On some installations the interface will be called Local Area Connection and on others it will be called Network Bridge. On our system it is called Network Bridge. Right-click on Network Bridge -> Properties.
- The Network Bridge Configuration, or Local Area Connection, panel is used to set TCP/IP protocol settings. In This connection uses the following items: box, click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click on Properties.The default setting is DHCP-enabled operation (i.e.“Obtain an IP address automatically”).Many network administrators will want to use DHCP to configure all client TCP/IP protocol stack settings.If it is necessary to provide a fixed IP address, click on “Use the following IP address” and enter the IP Address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway address in the boxes provided.
- Click the Advanced button to proceed with TCP/IP configuration. This opens a panel in which it is possible to create additional IP addresses for this interface. The technical name for the additional addresses is IP aliases, and additionally this panel permits the setting of more default gateways (routers). In most cases where DHCP is used, it will not be necessary to create additional settings.
Fixed settings may be required for DNS and WINS if these settings are not provided automatically via DHCP.
- Click the DNS tab to add DNS server settings. The example system uses manually configured DNS settings. When finished making changes, click the OK to commit the settings.DNS Configuration.
- Click the WINS tab to add manual WINS server entries. This step demonstrates an example system that uses manually configured WINS settings. When finished making changes, click OK to commit the settings.WINS Configuration
Network configuration in Linux
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 05:04 0 comments
OOPs Concepts
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 23:34 0 comments Tuesday, 9 July 2013
| OOPs – Object Oriented Programming System Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses “Objects “and their interactions to design applications and computer programs. There are different types of OOPs are used, they are
1) Object :Object is the basic unit of object-oriented programming. Objects are identified by its unique name. An object represents a particular instance of a class. There can be more than one instance of an object. Each instance of an object can hold its own relevant data.
An Object is a collection of data members and associated member functions also known as methods.
For example whenever a class name is created according to the class an object should be created without creating object can’t able to use class.
The class of Dog defines all possible dogs by listing the characteristics and behaviors they can have; the object Lassie is one particular dog, with particular versions of the characteristics. A Dog has fur; Lassie has brown-and-white fur.
2) Class :
Classes are data types based on which objects are created. Objects with similar properties and methods are grouped together to form a Class. Thus a Class represents a set of individual objects. Characteristics of an object are represented in a class as Properties. The actions that can be performed by objects become functions of the class and is referred to as Methods.
For example consider we have a Class of Cars under which Santro Xing, Alto and WaganR represents individual Objects. In this context each Car Object will have its own, Model, Year of Manufacture, Colour, Top Speed, Engine Power etc., which form Properties of the Car class and the associated actions i.e., object functions like Start, Move, Stop form the Methods of Car Class.No memory is allocated when a class is created. Memory is allocated only when an object is created, i.e., when an instance of a class is created.
|
Inheritance is the process of forming a new class from an existing class or base class.
- Single level inheritance
- Multi-level inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
- Hierarchial inheritance
Polymorphism allows routines to use variables of different types at different times. An operator or function can be given different meanings or functions. Polymorphism refers to a single function or multi-functioning operator performing in different ways.
It contains a concept of Inheritance and Polymorphism.
Setup The Timezone
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 06:47 0 comments
HowTo: Linux Server Change OR Setup The Timezone
Unix time, or POSIX time, is a system for describing points in time: it is the number of seconds elapsed since midnight UTC on the morning of January 1, 1970, not counting leap seconds. The definition for time zones can be written in short form as UTC±n (or GMT±n), where n is the offset in hours. You can use the following commands:
Command to change the Linux timezone
If you are using Fedora / RHEL / Cent OS Linux
# redhat-config-dateOR type setup and select time zone configuration. This tool is recommended for remote ssh text based sessions.
# setupSelect timezone configuration
Just follow on screen instructions to change the timezone.
If you are using Debian / Ubuntu Linux
# dpkg-reconfigure tzdataAgain, just follow on screen instructions.
Set timezone using /etc/localtime configuration file [any Linux distro]
Generic procedure to change timezone under Linux
# cd /etcCreate a symlink to file localtime:
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/EST localtimeOR some distro use /usr/share/zoneinfo/dirname/zonefile format (Red hat and friends):
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/EST localtimeOR if you want to set up it to IST (Asia/Calcutta):
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta localtimePlease note that in above example you need to use directory structure i.e. if you want to set the timezone to Calcutta (India) which is located in the Asia directory.
How do I verify new settings?
$ dateOutput:
Tue Aug 27 14:46:08 EST 2006
How do I use of environment variable called TZ?
$ export TZ=America/Los_Angeles
$ dateSample Output:
Thu Aug 27 11:10:08 PST 2006
Cluster configuration
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 06:40 0 comments
Red Hat Cluster allows you to connect a group of computers (called nodes or members) to work together as a cluster. It provides a wide variety of ways to configure hardware and software to suit your clustering needs (for example, a cluster for sharing files on a GFS file system or a cluster with high-availability service failover). This book provides information about how to use configuration tools to configure your cluster and provides considerations to take into account before deploying a Red Hat Cluster. To ensure that your deployment of Red Hat Cluster fully meets your needs and can be supported, consult with an authorized Red Hat representative before you deploy it.
List of web browsers
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 05:51 1 comments
List of web browsers
History:-
This is a table of personal computer web browsers by year of release of major version, in chronological order, with the approximate number of worldwide Internet users in millions. Note that Internet user data is related to the entire market, not the versions released in that year. The increased growth of the Internet in the 1990s and 2000s means that current browsers with small market shares have more total users than the entire market early on. For example, 90% market share in 1997 would be roughly 60 million users, but by the start of 2007 9% market share would equate to over 90 million users.
| Year | Web browsers | Internet users (in millions)[1][2][3] |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | WorldWideWeb (Nexus) | 4 |
| 1992 | ViolaWWW, Erwise, MidasWWW, MacWWW (Samba) | 7 |
| 1993 | Mosaic, Cello,[4] Lynx 2.0, Arena, AMosaic 1.0 | 10 |
| 1994 | IBM WebExplorer, Netscape Navigator, SlipKnot 1.0, MacWeb, IBrowse, Agora (Argo), Minuet | 20 |
| 1995 | Internet Explorer 1, Netscape Navigator 2.0, OmniWeb, UdiWWW,[5] Internet Explorer 2, Grail | 16-39 |
| 1996 | Arachne 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.0, Netscape Navigator 3.0, Opera 2.0, PowerBrowser 1.5,[6] Cyberdog, Amaya 0.9,[7] AWeb, Voyager | 36-73 |
| 1997 | Internet Explorer 4.0, Netscape Navigator 4.0, Netscape Communicator 4.0, Opera 3.0,[8] Amaya 1.0[7] | 70-118 |
| 1998 | iCab, Mozilla | 147-184 |
| 1999 | Amaya 2.0,[7] Mozilla M3, Internet Explorer 5.0 | 248-278 |
| 2000 | Konqueror, Netscape 6, Opera 4,[9] Opera 5,[10] K-Meleon 0.2, Amaya 3.0,[7] Amaya 4.0[7] | 361-396 |
| 2001 | Internet Explorer 6, Galeon 1.0, Opera 6,[11] Amaya 5.0[7] | 513-499 |
| 2002 | Netscape 7, Mozilla 1.0, Phoenix 0.1, Links 2.0, Amaya 6.0,[7] Amaya 7.0[7] | 587-659 |
| 2003 | Opera 7,[12] Safari 1.0, Epiphany 1.0, Amaya 8.0[7] | 719-771 |
| 2004 | Firefox 1.0, Netscape Browser, OmniWeb 5.0 | 817-897 |
| 2005 | Safari 2.0, Netscape Browser 8.0, Opera 8,[13] Epiphany 1.8, Amaya 9.0,[7] AOL Explorer 1.0, Maxthon 1.0, Shiira 1.0 | 1018-1022 |
| 2006 | SeaMonkey 1.0, K-Meleon 1.0, Galeon 2.0, Camino 1.0, Firefox 2.0, Avant 11, iCab 3, Opera 9,[14] Internet Explorer 7 | 1093-1150 |
| 2007 | Maxthon 2.0, Netscape Navigator 9, NetSurf 1.0, Flock 1.0, Safari 3.0, Conkeror | 1319-1364 |
| 2008 | Konqueror 4, Safari 3.1, Opera 9.5,[15] Firefox 3, Amaya 10.0,[7] Flock 2, Chrome 1, Amaya 11.0[7] | 1574-1556 |
| 2009 | Internet Explorer 8, Chrome 2-3, Safari 4, Opera 10,[16] SeaMonkey 2, Camino 2, Firefox 3.5 | 1802-1743 |
| 2010 | K-Meleon 1.5.4, Firefox 3.6, Chrome 4-8, Opera 10.50,[17] Safari 5, xxxterm, Opera 11 | 1971-2012 |
| 2011 | Chrome 9-16, Firefox 4-9, Internet Explorer 9, Maxthon 3.0, SeaMonkey 2.1-2.3, Opera 11.50, Safari 5.1 | 2,267-2264 |
| 2012 | Chrome 17-23, Firefox 10-17, Internet Explorer 10, Opera 12, Safari 6 | 2,405 |
A Comparison of Network Models
Posted by HEMANT KUSHWAHA at 05:59 0 comments Saturday, 6 July 2013
A Comparison of Network Models
Blogroll
Blogger templates
Blogroll
Blogger news
Blogger templates
Blogger news
Social Icons
Social Icons
-
Less Infrastructure, More Intelligent Servers Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) and servers unify computing, networking, mana...
-
CISCO ROUTER SERIES The industry’s most widely deployed universal services aggregation router for enterprise and service provider ...
-
List of web browsers History:- This is a table of personal computer web browsers by year of release of major version, in ch...
-
A Comparison of Network Models There are two network models that describe how networks 'work'. The OSI Model , the older model,...
-
OOPs – Object Oriented Programming System Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses “Objects “and the...
-
RSA Algorithm Example Choose p = 3 and q = 11 Compute n = p * q = 3 * 11 = 33 Compute φ(n) = (p - 1) * (q - 1) = 2 * 10 = 20 Ch...
-
HowTo: Linux Server Change OR Setup The Timezone by NIXCRAFT on AUGUST 27, 2006 · 55 COMMENTS · LAST UPDATED NOVEMBER 5, 201...
-
CREAT BACKDOOR :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::...
-
THE CRYPTOGRAPHY GUIDE Cryptographic Algorithms There are of course a wide range of cryptographic algorithms in use. The f...
-
Using Wine In Red Hat Linux Wine is a great tool for Linux users who want to install and run Windows ...
Blog Archive
-
▼
2013
(25)
-
▼
July
(15)
- HOW TO CREAT BACKDOOR IN WINDOW SEVEN
- Using Wine In Red Hat Linux
- To Password Protect Folders with Folder Protector?
- RSA Algorithm Example
- Cryptographic Algorithms
- Windows XP Network configuration
- Network configuration in Linux
- OOPs Concepts
- Setup The Timezone
- Cluster configuration
- List of web browsers
- A Comparison of Network Models
- CLOUD COMPUTING
- Basic Linux Commands
- STEGANOGRAPHY
-
▼
July
(15)


.jpg)

.jpg)














.jpg)
